Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Trauma Inj > Volume 36(4); 2023 > Article
-
Original Article
Outcomes and physiologic responses associated with ketamine administration after traumatic brain injury in the United States and Canada: a retrospective analysis -
Austin J. Peters, MD1
 , Saad A. Khan, MS2
, Saad A. Khan, MS2 , Seiji Koike, MAS3
, Seiji Koike, MAS3 , Susan Rowell, MD4
, Susan Rowell, MD4 , Martin Schreiber, MD5
, Martin Schreiber, MD5
-
Journal of Trauma and Injury 2023;36(4):354-361.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.20408/jti.2023.0034
Published online: November 7, 2023
- 941 Views
- 45 Download
1Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA
2Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE, USA
3Biostatistics and Design Program, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA
4Department of Surgery, Section of Trauma, University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA
5Donald D. Trunkey Center for Civilian and Combat Casualty Care, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA
- Correspondence to Austin J. Peters, MD Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, 3181 SW Sam Jackson Park Rd, Mail Code L459 Portland, OR 97239-3098, USA Tel: +1-503-494-4047 Email: peterau@ohsu.edu
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Traumatology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Purpose
- Ketamine has historically been contraindicated in traumatic brain injury (TBI) due to concern for raising intracranial pressure. However, it is increasingly being used in TBI due to the favorable respiratory and hemodynamic properties. To date, no studies have evaluated whether ketamine administered in subjects with TBI is associated with patient survival or disability.
-
Methods
- We performed a retrospective analysis of data from the multicenter Prehospital Tranexamic Acid Use for Traumatic Brain Injury trial, comparing ketamine-exposed and ketamine-unexposed TBI subjects to determine whether an association exists between ketamine administration and mortality, as well as secondary outcome measures.
-
Results
- We analyzed 841 eligible subjects from the original study, of which 131 (15.5%) received ketamine. Ketamine-exposed subjects were younger (37.3±16.9 years vs. 42.0±18.6 years, P=0.037), had a worse initial Glasgow Coma Scale score (7±3 vs. 8±4, P=0.003), and were more likely to be intubated than ketamine-unexposed subjects (88.5% vs. 44.2%, P<0.001). Overall, there was no difference in mortality (12.2% vs. 15.5%, P=0.391) or disability measures between groups. Ketamine-exposed subjects had significantly fewer instances of elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) compared to ketamine-unexposed subjects (56.3% vs. 82.3%, P=0.048). In the very rare outcomes of cardiac events and seizure activity, seizure activity was statistically more likely in ketamine-exposed subjects (3.1% vs. 1.0%, P=0.010). In the intracranial hemorrhage subgroup, cardiac events were more likely in ketamine-exposed subjects (2.3% vs. 0.2%, P=0.025). Ketamine exposure was associated with a smaller increase in TBI protein biomarker concentrations.
-
Conclusions
- Ketamine administration was not associated with worse survival or disability despite being administered to more severely injured subjects. Ketamine exposure was associated with reduced elevations of ICP, more instances of seizure activity, and lower concentrations of TBI protein biomarkers.
- Background
- Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic with unique pharmacologic effects compared to other anesthetic induction agents [1]. Early studies of ketamine’s physiology identified potentially harmful side effects associated with its administration including increased intracranial pressure (ICP) [2,3], increased cerebral blood flow [4], and increased cerebral metabolic rate [5]. Based on these reports, use of ketamine for traumatic brain injury (TBI) has traditionally been discouraged.
- Despite these initial concerns, ketamine’s favorable hemodynamic, analgesic, and respiratory sparing effects have led to it increasingly being utilized in trauma patients including those with TBI [6]. Ketamine’s effects on ICP have been directly investigated in small-scale studies which found either no effect on ICP or reduced ICP when ketamine was prospectively administered to TBI subjects. In addition to its potential impact on ICP, ketamine has also been proposed as a neuroprotective agent in TBI based on its reduction in postinjury glutamate toxicity [7,8] and inhibition of cortical spreading depressions [9]. Notably, none of these studies explored subject outcomes and thus, there is a lack of clarity related to ketamine’s ICP effects and patient outcomes.
- Objectives
- The TXA for TBI (Prehospital Tranexamic Acid Use for Traumatic Brain Injury) trial was a large, multinational, multicenter, randomized controlled trial that provided the opportunity to evaluate an extensive sample of TBI subjects and associated outcomes [10]. Using the dataset from this study, we examined the characteristics of ketamine administration in the TBI population to analyze ketamine’s association with morbidity and mortality, as well as physiologic responses including ICP and longitudinal TBI biomarker trajectories. We hypothesized that ketamine exposure would not be associated with worse survival or disability after TBI, and that the physiologic responses and TBI-related biomarker responses would not be different between ketamine-exposed and ketamine-unexposed TBI subjects in the TXA for TBI trial population.
INTRODUCTION
- Ethics statement
- The original study [10] was approved by the Institutional Review Board for the study’s associated Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium Clinical Trials Center at the University of Washington. Informed consent was not possible for all participants initially and therefore enrollment was conducted under US regulations for Exception from Informed Consent Requirements for Emergency Research as well as the Canadian Tri-County Policy Statement 2, and informed consent was obtained as soon as feasible. The original study is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov (identifier: NCT01990768).
- Study design
- The TXA for TBI trial was a multicenter, North American randomized, controlled trial that enrolled subjects from May 2015 until November 2017 [10]. Subjects with moderate-to-severe TBI were randomized to placebo bolus prehospital and 8-hour placebo infusion in-hospital, a 2-g tranexamic acid (TXA) prehospital bolus followed by an 8-hour placebo infusion in the hospital, or a 1-g prehospital bolus followed by a 1-g in-hospital 8-hour infusion. In the primary trial, there were no significant differences in mortality or morbidity between groups overall, however, in the subset of subjects with intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), prehospital administration of a 2-g bolus of TXA bolus was associated with decreased mortality [8,10].
- Participants
- We performed a retrospective analysis of the TXA for TBI trial dataset for ketamine exposure to examine the associations between ketamine and clinical and laboratory outcomes in subjects with TBI. Ketamine exposure was defined as recorded ketamine administration by emergency medical services in the prehospital setting; exact dosing and timing of the ketamine administration was not available. Subjects without ketamine exposure data were excluded.
- Demographic measures
- Demographics variables included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), weight, initial Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, initial Injury Severity Score (ISS), history of seizure, intubation status, presence of ICH, and TXA study group allocation.
- Death and disability outcome measures
- The primary outcome assessed was death within 6 months of injury; secondary outcomes included the Glasgow Outcome Scale Extended (GOSE) and Disability Rating Scale (DRS) scores at discharge and 6 months postinjury, as well as incidences of seizure activity, cardiac events (cardiac arrest or heart failure), and surgical interventions.
- Physiologic outcome measures
- Physiologic outcome measures included the following: systolic blood pressure (SBP), heart rate and temperature, PaO2, and ICP. Measurements were taken from the first 24 hours following hospital presentation. ICP was measured with either a Camino (Natus Medical Inc) intracranial pressure and temperature monitor or an external ventricular drain pressure monitor. ICP elevation was defined as ICP >20 cmH2O; bradycardia was defined as heart rate <60 beats per minute (bpm) and tachycardia as heart rate >100 bpm; hypoxia was defined as PaO2 <80 mmHg; hypotension was defined as SBP <90 mmHg and hypertension defined as SBP >180 mmHg; hypothermia was defined as <35 °C and hyperthermia as >38 °C.
- TBI protein biomarker measures
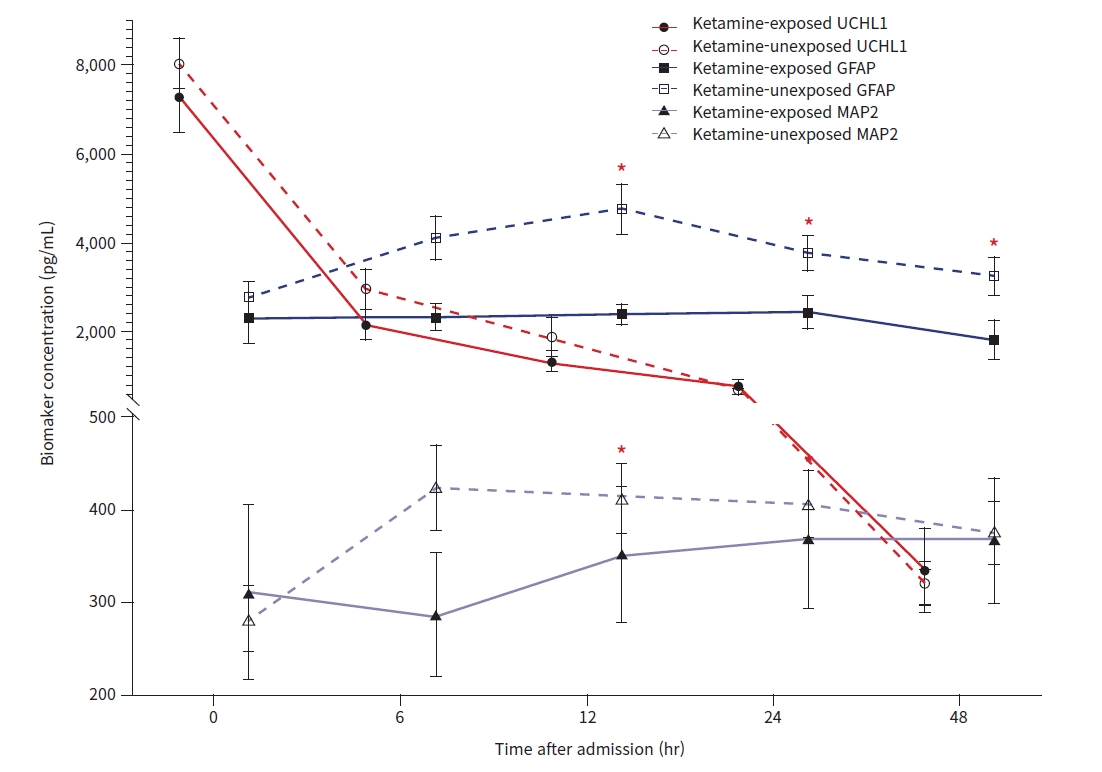
- The TXA for TBI trial performed longitudinal biomarker measurements of the TBI-related biomarkers glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) [8]. Serum concentration measurements of GFAP, MAP2, and UCHL1 were compared between the ketamine-exposed and ketamine-unexposed groups at admission, 6-, 12-, 24-, and 48-hours following hospital admission [11]. Biomarkers were compared using the change in measured serum concentration from admission to each subsequent time point, as well as a comparison of biomarker concentrations at each time point.
- ICH subgroup
- Based on the decreased mortality observed in the original TXA for TBI trial [10] in the ICH subgroup of the 2-g TXA arm, we performed a subgroup analysis of ICH subjects comparing ketamine exposure groups.
- Statistical analysis
- Demographic variables were assessed for their association with outcomes including our primary outcome of death within 6 months of injury. The P-value for significance of variables was set at P<0.05. A multivariate mixed-effects logistic regression model was created using the variables age, sex, race, BMI, seizure history, intubation status, and TXA study assignment to evaluate the association of ketamine administration on morbidity, mortality, and vital signs outcomes, for both the entire cohort and for the ICH subgroup analysis. Because there were very few instances of cardiac events and seizure activity, a simplified statistical model was created to analyze both outcomes in the entire cohort and the ICH subgroup. For cardiac events in the entire cohort, sex and race were removed from the model; for seizure activity in this same cohort, only race was removed. For ICH subgroup cardiac events, only BMI and intubation status were used as covariates; for seizure activity in the ICH subgroup analysis, sex, BMI, seizure history, and intubation status were used as covariates. To evaluate the association of ketamine exposure with TBI-related protein biomarkers, biomarker data were log-transformed, and a mixed-effects model was created using the same demographic variables (age, sex, race, BMI, seizure history, intubation status, and TXA study arm); final P-values in this model were adjusted for multiple comparisons using Bonferroni correction. All results are provided as mean±standard deviation unless otherwise specified. TBI was stratified into severe (GCS ≤8), moderate (GCS 9–12) and mild (GCS 13–15); ISS was stratified into severe (>25), moderate (16–25), and mild (≤15); GOSE was stratified into poor recovery (1–4) and good recovery (5–8); DRS was stratified into mild (0–1), moderate (2–6), severe (7–11), and vegetative or worse (≥12). Statistical analyses were completed using Stata ver. 17.0 (Stata Corp).
METHODS
- Demographics and clinical characteristics
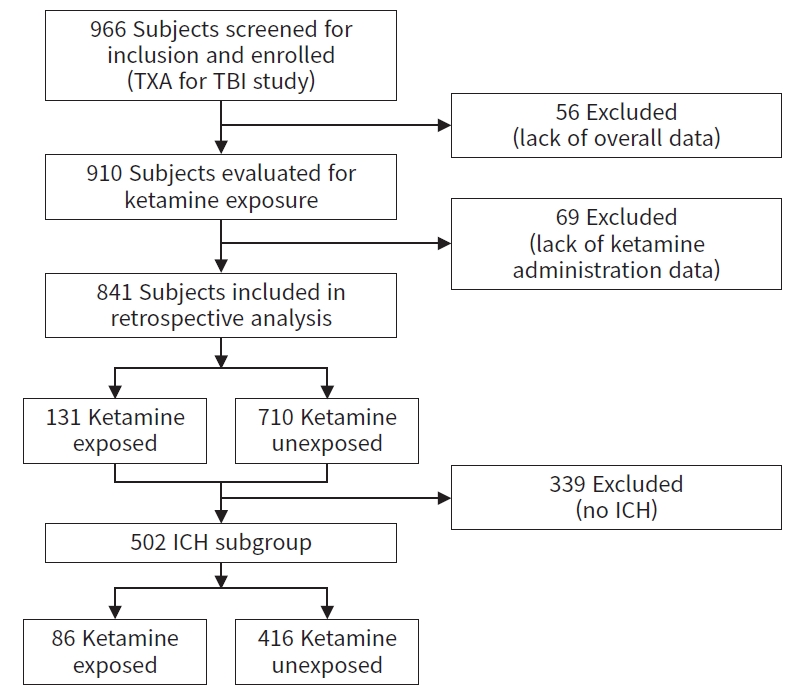
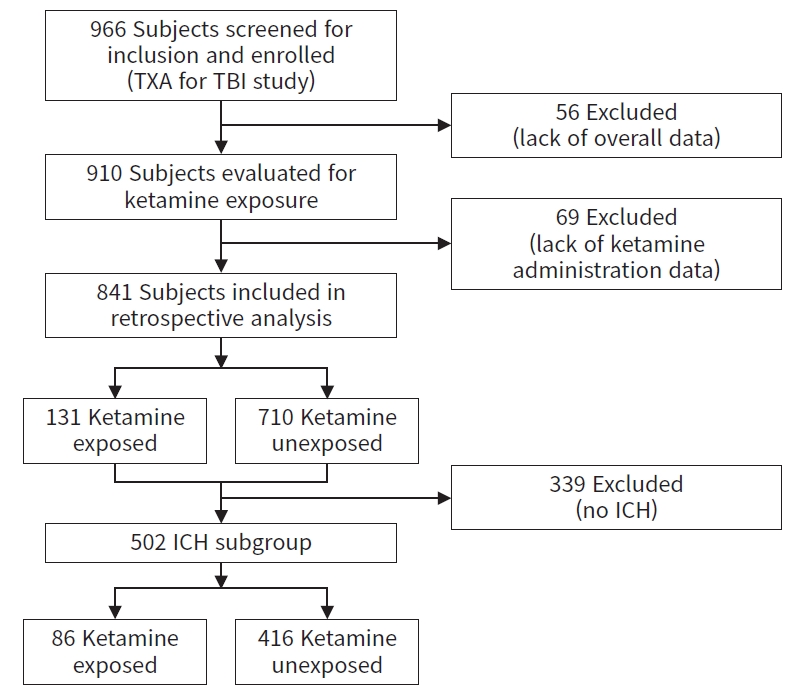
- Of the 966 subjects included in the primary analysis in the original TXA for TBI trial, 910 had complete data collected and were analyzed for ketamine exposure; 69 subjects lacked ketamine administration information and were excluded, leaving 841 subjects for our analysis. Of these subjects, 131 (15.6%) received ketamine and 710 (84.4%) did not receive ketamine (Fig. 1).
- Demographic and clinical characteristics of the ketamine-exposed and ketamine-unexposed subjects are listed in Table 1. Overall, the ketamine-exposed group was younger (37.3±16.9 years vs. 42.0±18.6 years, P=0.037); the groups otherwise had similar sex- and race-distribution, BMI, and TXA study allocations. Ketamine-exposed subjects had a worse initial GCS (7±3 vs. 8±4, P=0.003) and were more likely to be intubated (88.5% vs. 44.2%, P<0.001); initial ISS and ICH status were not different between groups.
- Death and disability
- In our primary outcome of death at any time, there was no difference between the ketamine-exposed and the ketamine-unexposed groups (mortality rate: ketamine exposed, 12.2% vs. ketamine unexposed, 15.5%; P=0.391) (Table 2).
- For our secondary outcomes, there was similarly no difference in disability scores for GOSE at discharge (ketamine exposed, 3.9±2.1 vs. ketamine unexposed, 4.3±2.4; P= 0.967) or at 6-months postinjury (ketamine exposed, 5.4±2.4 vs. ketamine unexposed, 5.4±2.7; P=0.221) and DRS at discharge (ketamine exposed, 8.8±9.7 vs. ketamine unexposed, 8.3±10.3; P=0.324) or at 6-months postinjury (ketamine exposed, 5.8±9.9 vs. ketamine unexposed, 7.0 ± 11.2; P=0.151). There was no difference in the need for surgical intervention between groups (ketamine exposed, 6.9% vs. ketamine unexposed, 11.1%; P=0.113). Using a simplified statistical model due to very few instances, ketamine exposure was significantly more likely to be associated with seizure activity (3.1% vs. 1.0%, P=0.010); ketamine exposure was not associated with a higher rate of cardiac events (1.5% vs. 0.8%, P=0.961) (Table 2).
- Physiologic response
- Elevated intracranial pressure was significantly less frequent in the ketamine-exposed group (instances of ICP elevation, 56.3% vs. 82.3%; P=0.048). Instances of hypoxia, and extremes of heart rate, SBP, and temperature were similar between groups (Table 3).
- TBI biomarker trajectories
- Ketamine exposure was associated with significantly smaller changes in concentration for GFAP at 12-, 24-, and 48-hours following admission and for MAP2 at 12- and 24-hours following admission. UCHL1 changes from baseline were not significantly different between groups at any time point (Fig. 2). There were no differences in biomarker concentrations when compared against each other at any time point after correcting for multiple comparisons (Table 4).
- ICH subgroup analysis
- Of 841 subjects with ketamine exposure data, 502 subjects (59.7%) had a radiographically confirmed ICH, 86 of 131 (65.6%) in the ketamine-exposed group and 416 of 710 (58.6%) in the ketamine-unexposed group (Fig. 1). Demographic characteristics and TXA study group distribution were similar to the entire cohort, including a significant age difference (ketamine exposed, 38.1±17.5 years vs. ketamine unexposed, 42.0±18.8 years; P=0.030) and a significantly higher percentage of intubated subjects in the ketamine-exposed group (90.7% vs. 53.8%, P<0.001). GCS was not significantly different in the ICH subgroup (ketamine exposed, 6±3 vs. ketamine unexposed, 7±3; P=0.086); all other demographic variables were similar to the entire cohort (Table S1).
- Mortality in the ICH subgroup was higher than in the entire cohort but there was again no difference between ketamine exposure groups (ketamine exposed, 18.6% vs. ketamine unexposed, 23.3%; P=0.177). There were no differences in GOSE or DRS measurements between groups, and no difference in surgical intervention (Table S2). Using a simplified model, ketamine exposure continued to be associated with increased seizure activity (3.5% vs. 1.0%, P = 0.009); cardiac events were also associated with ketamine exposure (2.3% vs. 0.2%, P = 0.025).
- Physiologic responses were similar to the entire cohort as well, but no statically significant difference in ICP was observed in this subgroup analysis (ketamine exposed, 56.3% vs. ketamine unexposed, 82.0% with an instance of elevated ICP; P=0.055) (Table S3).
- Biomarker trajectories in the ICH subgroup were similar to the entire cohort, including a smaller increase from baseline for the biomarkers GFAP and MAP2 at similar time points, and no differences in UCHL1 between groups (Fig. S1). At the 48-hour time point, GFAP concentration was lower in the ketamine-exposed group (2,261±4,727 pg/mL vs. 4,497±10,508 pg/mL, P=0.003) (Table S4).
RESULTS
- In this retrospective analysis of a large, multinational, multicenter trial, ketamine was administered to 15.5% of all subjects sustaining TBI. It is notable that a significant number of subjects with TBI received ketamine in this large clinical trial involving 12 centers and almost 40 emergency medical services agencies, despite ketamine’s traditional avoidance in TBI. In our analysis, ketamine-exposed subjects had a more severe head injury profile based on initial GCS and intubation status yet had no differences in survival or disability. An important qualification of these data is that the ketamine-unexposed group was on average 5 years older than the ketamine-exposed subjects, and older age is associated with worse outcomes after TBI [12]. However, no prior studies have examined ketamine’s association with morbidity and mortality after TBI, and these findings, especially taken in context of the higher injury severity, are reassuring given the frequency of use of ketamine in patients with TBI.
- There remain important safety considerations in the use of ketamine in patients with TBI given our findings associating its use with cardiovascular events and seizure activity. Seizure activity was significantly associated with ketamine administration in both the entire cohort as well as in the ICH subgroup, and ketamine administration was significantly associated with cardiac events in the ICH subgroup. However, these were rare events, and at this time it remains unclear whether the association between seizure activity and ketamine administration is due to the worse injury profile of the ketamine-exposed group or can be attributed to the administration of ketamine itself. Notably, ketamine has been shown to be associated with cardiovascular collapse in other patient populations [13]. Any administration of ketamine should continue to consider its cardiovascular and neurological side effects.
- In this study, we found that ketamine administration was associated with a decrease in the frequency of elevated ICP, which is in contrast to the traditionally accepted association of ketamine and increased ICP [3]. Early studies examining ketamine’s effects on ICP had notable limitations that may explain their findings: study subjects were healthy volunteers without TBI, and respiratory rate was not controlled, which is notable as ketamine does reduce respiratory rate, which has the potential to impact ICP [2]. Another important consideration is that we only analyzed instances of extremes in ICP and not duration or severity of the ICP response. Our findings associating ketamine administration with reduced instances of elevated ICP are consistent with the few clinical studies that have explored ketamine’s effects directly in subjects with TBI, which have shown that ketamine either had no effect on ICP [14,15] or reduced ICP.
- Finally, the longitudinal circulating biomarkers of brain injury examined in the original TXA for TBI trial presented a unique opportunity to evaluate the effect that ketamine had on the trajectory of these biomarkers. By examining the changes in the concentrations at multiple time points, we observed a potential suppressive effect from ketamine administration in that ketamine exposure was associated with a reduced rise in both GFAP and MAP2 concentrations at all time points, and a significantly reduced GFAP concentration at 48-hours postinjury in the ICH subgroup. Based on our previous observations that these biomarker concentrations are positively associated with injury severity [8], this suppressive effect associated with ketamine exposure warrants further investigation. Furthermore, these data support the potential utility of using longitudinal TBI biomarker trajectories to monitor pharmacologic effect and therapeutic responses associated with ketamine administration [8].
- Limitations
- The primary limitation of this study is the retrospective collection of these prospectively collected data which therefore limits our findings to associations between ketamine exposure and outcomes rather than establishing a causal relationship. Furthermore, ICP was measured in fewer than 20% of subjects which limits our power to draw conclusions. Finally, complete details regarding the dose and timing of ketamine administration were not available and physiologic responses were limited to instances of extremes.
- Conclusions
- This retrospective analysis of a multinational, multicenter TXA for TBI trial, ketamine administration was not associated with increased mortality or disability and was associated with fewer instances of elevated ICP, despite being administered to more severely injured subjects. Further prospective studies related to the association between ketamine administration and clinical outcomes and physiologic measures especially longitudinally collected protein biomarkers are warranted.
DISCUSSION
-
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
The primary study (Prehospital Tranexamic Acid Use for Traumatic Brain Injury trial) was supported by a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (No. NHLBI 5R01HL126585-02). The traumatic brain injury biomarker collection portion of the primary study was supported by a grant from the Defense Medical Research and Development Program (No. W81XWH-12-CCCJPC-TACR).
-
Data availability
Data analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization: AJP, MS; Data curation: AJP, SAK, SK; Formal analysis: AJP, SK; Funding acquisition: AJP, SR, MS; Investigation: AJP, SR, MS; Methodology: AJP, SK; Project administration: AJP; Visualization: AJP, SK; Writing–original draft: AJP, SAK; Writing–review & editing: all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Table S1.
Table S2.
Fig. S1.
| Characteristic |
Ketamine exposure |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed (n=131) | Unexposed (n=710) | ||
| Age (yr) | 37.3±16.9 | 42.0±18.6 | 0.037* |
| Male sex | 101 (77.1) | 526 (74.1) | 0.586 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.0±5.8 | 26.3±5.6 | 0.236 |
| Race | 0.546 | ||
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 1 (0.8) | 16 (2.3) | |
| Black | 11 (8.4) | 93 (13.1) | |
| Native American | 0 | 2 (0.3) | |
| White | 68 (51.9) | 324 (45.6) | |
| Unknown | 49 (37.4) | 267 (37.6) | |
| GCS score | 7±3 | 8±4 | 0.003* |
| Injury Severity Score | 20.7±13.6 | 18.8±13.1 | 0.142 |
| Prior seizure history | 5 (3.8) | 36 (5.1) | 0.695 |
| Intubated on scene | 116 (88.5) | 314 (44.2) | <0.001* |
| ICH presence | 86 (65.6) | 416 (58.6) | 0.179 |
| TXA allocation group | 0.798 | ||
| Placebo | 45 (34.4) | 227 (32.0) | |
| 1 g | 38 (29.0) | 225 (31.7) | |
| 2 g | 48 (36.6) | 258 (36.3) | |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
Baseline characteristics and group allocations were similar between groups, however ketamine-exposed subjects were younger, with a worse initial GCS and were more likely to be intubated.
GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; ICH, intracranial hemorrhage; TXA, tranexamic acid.
* P<0.05.
| Variable |
Ketamine exposure |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed (n=131) | Unexposed (n=710) | ||
| Death at any time | 16 (12.2) | 110 (15.5) | 0.391 |
| Seizure activity | 4 (3.1) | 7 (1.0) | 0.010a)* |
| Cardiac events | 2 (1.5) | 6 (0.8) | 0.961a) |
| Required surgical intervention | 9 (6.9) | 79 (11.1) | 0.113 |
| Glasgow Outcomes Score Extended | |||
| At discharge | 3.9±2.1 | 4.3±2.4 | 0.967 |
| At 6 mo | 5.4±2.4 | 5.4±2.7 | 0.221 |
| Disability Rating Scale | |||
| At discharge | 8.8±9.7 | 8.3±10.3 | 0.324 |
| At 6 mo | 5.8±9.9 | 7.0±11.2 | 0.151 |
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation. Morbidity and mortality outcomes were similar between groups, with no differences in death or measures of disability between groups. Ketamine exposure was associated with more seizure activity.
a) Variables analyzed using a simplified statistical model due to few overall occurrences.
* P<0.05.
| Variable |
Ketamine exposure |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed (n=131) | Unexposed (n=710) | ||
| ICP >20 mmHg (n=140) | 9/16 (56.3) | 102/124 (82.3) | 0.048* |
| Hypoxia PaO2 <80 mmHg | 48 (36.6) | 246 (34.6) | 0.819 |
| Hypothermia (temperature ≤35 ˚C) | 23 (17.6) | 44 (6.2) | 0.119 |
| Hyperthermia (temperature ≥38 ˚C) | 0 | 7 (1.0) | 0.477 |
| Heart rate | |||
| Bradycardic (<60 bpm) | 18 (13.7) | 93 (13.1) | 0.937 |
| Tachycardic (>100 bpm) | 64 (48.9) | 347 (48.9) | >0.999 |
| Systolic blood pressure | |||
| Hypotensive (<90 mmHg) | 19 (14.5) | 74 (10.4) | 0.557 |
| Hypertensive (>180 mmHg) | 20 (15.3) | 135 (19.0) | 0.337 |
Values are presented as number (%). Physiologic measures compared between groups demonstrated that ketamine exposure was associated with fewer recorded measurements of elevated ICP; there were no other statistically significant differences between the groups.
ICP, intracranial pressure; bpm, beats per minute.
* P<0.05
- 1. Natoli S. The multiple faces of ketamine in anaesthesia and analgesia. Drugs Context 2021;10:2020-12-8. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Lorhan PH, Lippmann M. A clinical appraisal of the use of ketamine hydrochloride in the aged. Anesth Analg 1971;50:448–51. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Wyte SR, Shapiro HM, Turner P, Harris AB. Ketamine-induced intracranial hypertension. Anesthesiology 1972;36:174–6. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Gardner AE, Olson BE, Lichtiger M. Cerebrospinal-fluid pressure during dissociative anesthesia with ketamine. Anesthesiology 1971;35:226–8. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Schwedler M, Miletich DJ, Albrecht RF. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism following ketamine administration. Can Anaesth Soc J 1982;29:222–6. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Chang LC, Raty SR, Ortiz J, Bailard NS, Mathew SJ. The emerging use of ketamine for anesthesia and sedation in traumatic brain injuries. CNS Neurosci Ther 2013;19:390–5. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Bhutta AT, Schmitz ML, Swearingen C, et al. Ketamine as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory agent in children undergoing surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass: a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2012;13:328–37. PubMed
- 8. Peters AJ, Schnell E, Saugstad JA, Treggiari MM. Longitudinal course of traumatic brain injury biomarkers for the prediction of clinical outcomes: a review. J Neurotrauma 2021;38:2490–501. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Carlson AP, Abbas M, Alunday RL, Qeadan F, Shuttleworth CW. Spreading depolarization in acute brain injury inhibited by ketamine: a prospective, randomized, multiple crossover trial. J Neurosurg 2018;1–7. Article
- 10. Rowell SE, Meier EN, McKnight B, et al. Effect of out-of-hospital tranexamic acid vs placebo on 6-month functional neurologic outcomes in patients with moderate or severe traumatic brain injury. JAMA 2020;324:961–74. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Anderson TN, Hwang J, Munar M, et al. Blood-based biomarkers for prediction of intracranial hemorrhage and outcome in patients with moderate or severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2020;89:80–6. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. McIntyre A, Mehta S, Aubut J, Dijkers M, Teasell RW. Mortality among older adults after a traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis. Brain Inj 2013;27:31–40. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Gelissen HP, Epema AH, Henning RH, Krijnen HJ, Hennis PJ, den Hertog A. Inotropic effects of propofol, thiopental, midazolam, etomidate, and ketamine on isolated human atrial muscle. Anesthesiology 1996;84:397–403. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Kolenda H, Gremmelt A, Rading S, Braun U, Markakis E. Ketamine for analgosedative therapy in intensive care treatment of head-injured patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1996;138:1193–9. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Bourgoin A, Albanese J, Leone M, Sampol-Manos E, Viviand X, Martin C. Effects of sufentanil or ketamine administered in target-controlled infusion on the cerebral hemodynamics of severely brain-injured patients. Crit Care Med 2005;33:1109–13. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

 KST
KST

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite